In most parts of the world, it’s still easier to buy a drink than it is to legally enjoy cannabis—even in regions where marijuana is partially legalized. Alcohol has long been socially accepted, deeply embedded in culture, celebrations, and stress relief routines. Cannabis, on the other hand, has carried decades of stigma despite growing scientific evidence highlighting its medical and therapeutic potential.
As laws evolve and misinformation gives way to research-backed insights, more people are asking an important question:
How does drinking alcohol compare to smoking or consuming cannabis when it comes to effects on the body and mind?
This guide breaks down the short-term and long-term effects of alcohol vs cannabis, their impact on physical health, mental well-being, social behavior, and medical use—so you can make informed, responsible decisions.
Understanding Alcohol: How it Affects the Body
Alcohol is classified as a central nervous system depressant. While often consumed socially or recreationally, its effects go far beyond relaxation.
Short-Term Effects of Alcohol
- Reduced inhibitions and increased sociability
- Slower reaction time and impaired judgment
- Temporary stress relief or emotional numbness
- Dehydration and disrupted sleep
- Impaired coordination and balance
Many people drink to unwind, reduce anxiety, or detach from daily pressures. However, these effects are temporary and often followed by fatigue, irritability, or low mood.
Long-Term Effects of Alcohol
Chronic or excessive alcohol consumption has been strongly linked to:
- Liver disease and fatty liver syndrome
- Cardiovascular issues and high blood pressure
- Increased risk of depression and anxiety
- Dependency and addiction
- Cognitive decline and memory impairment
Alcohol is also classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning it is directly linked to cancer risk when consumed regularly.
Understanding Cannabis: How it Affects the Body
Cannabis interacts with the body through the endocannabinoid system (ECS)—a regulatory system responsible for balance in mood, pain, sleep, immune response, and appetite.
Unlike alcohol, cannabis effects vary significantly based on:
- Strain type
- THC and CBD levels
- Method of consumption
- Individual tolerance and physiology
Indica vs Sativa: General Effects
Although modern science recognizes hybrid dominance, traditional classifications still help explain user experiences.
Indica-dominant strains are often associated with:
- Deep relaxation
- Stress reduction
- Pain relief
- Improved sleep
Sativa-dominant strains are often associated with:
- Increased energy
- Enhanced focus and creativity
- Mood elevation
- Reduced social anxiety
Medical Cannabis and High-CBD Strains
One of the most significant differences between alcohol and cannabis lies in medical application.
High-CBD (low-THC) strains are widely used to support individuals with conditions such as:
- Epilepsy and seizure disorders
- PTSD and anxiety disorders
- Chronic pain and inflammation
- Autism spectrum conditions
- Cancer-related symptoms
- Autoimmune diseases
- Neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s
CBD is non-intoxicating and does not produce a “high,” making it suitable for therapeutic use without cognitive impairment.
Smoking Cannabis: Risks vs Potential Benefits
Smoking anything introduces combustion-related risks, and cannabis is no exception. However, cannabis smoke differs chemically from tobacco smoke.
Potential Negative Effects
- Temporary airway irritation
- Short-term memory impairment (THC-related)
- Increased heart rate shortly after use
Research Insights
Interestingly, a well-cited 2008 study suggested that cannabis smoke may not carry the same lung cancer risk as tobacco smoke—and may even show protective effects due to cannabinoids’ anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties. Research is still evolving, and conclusions remain cautious.
Important note: Many users now prefer non-smoking methods such as vaporizers, edibles, tinctures, or capsules to minimize respiratory impact.

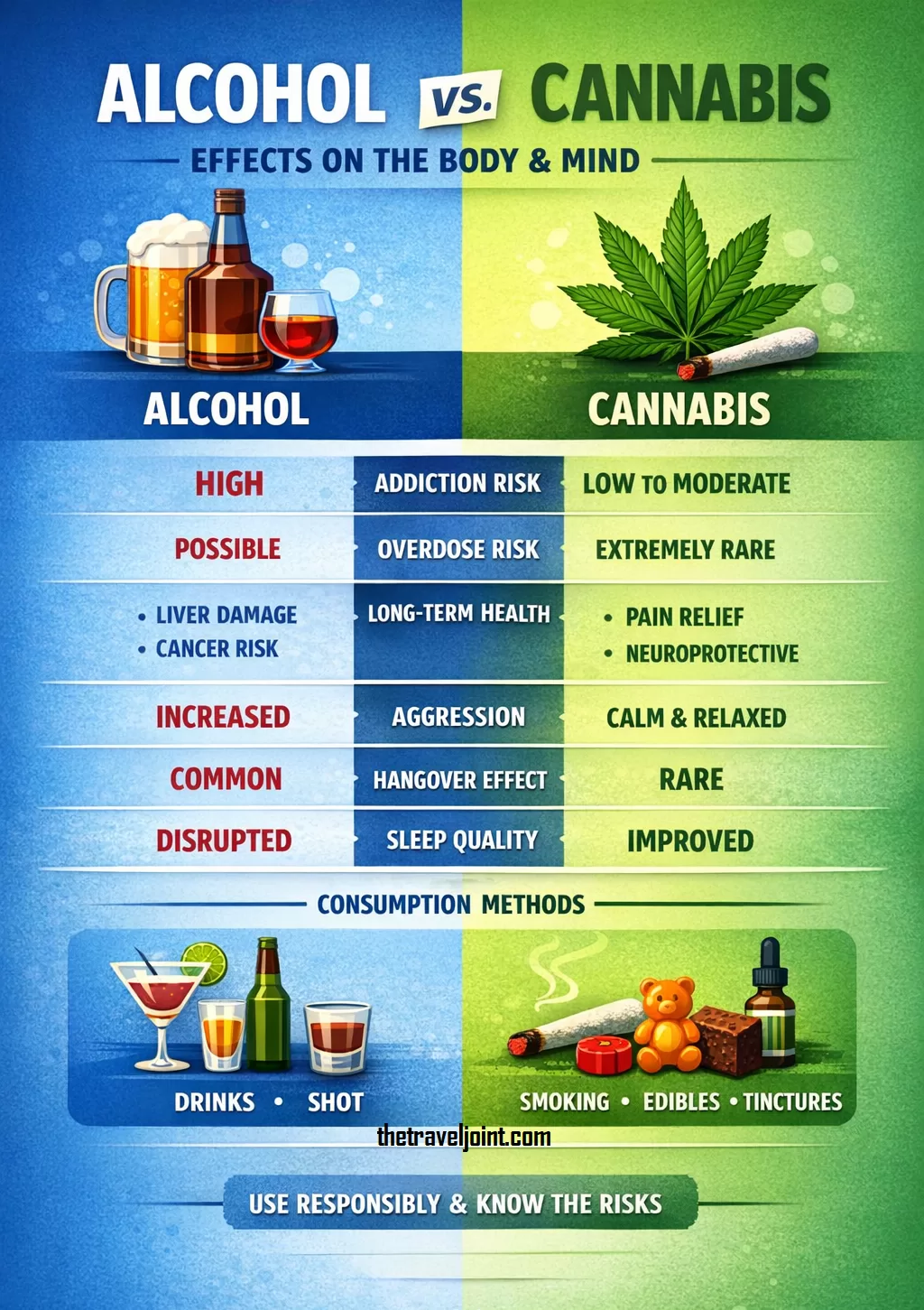
Alcohol vs Cannabis: Direct Comparison
| Aspect | Alcohol | Cannabis |
| Addiction Risk | High | Moderate to Low |
| Overdose Risk | Yes | Extremely rare |
| Medical Use | Limited | Extensive |
| Aggression Increase | Common | Rare |
| Liver Damage | Yes | No direct link |
| Hangover Effect | Common | Rare |
| Sleep Quality | Disrupted | Often improved |
Moderation Matters: The Golden Rule
Both alcohol and cannabis can cause negative side effects if abused. The key difference lies in dose control and awareness.
Responsible Use Tips
- Consume in moderation
- Avoid mixing substances
- Understand strain characteristics before use
- Choose consumption methods wisely
- Pay attention to mental and physical responses
Being strain-wise with cannabis and quantity-aware with alcohol significantly reduces risks.
Final Thoughts: Facts Over Fiction
Alcohol and cannabis are fundamentally different substances with different risk profiles, biological mechanisms, and long-term impacts.
While alcohol remains more socially accepted, research increasingly shows that cannabis—when used responsibly—may offer lower overall health risks and meaningful medical benefits.
That said, scientific research on cannabis is still limited due to legal restrictions. As declassification expands, clearer answers will continue to emerge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is cannabis safer than alcohol?
Current research suggests cannabis carries fewer long-term health risks than alcohol when used responsibly, but individual reactions vary.
Can cannabis help with anxiety?
Certain strains and CBD-dominant products may help reduce anxiety, while high-THC strains may increase it in some individuals.
Is smoking cannabis harmful to the lungs?
Smoking can irritate airways, but alternatives like vaporizing or edibles reduce respiratory risks.
Can you overdose on cannabis?
Fatal overdose from cannabis alone is extremely rare, unlike alcohol.
Should cannabis be used daily?
Medical use should be guided by healthcare professionals. Recreational use should remain moderate.
